

The factors that affect the efficiency of a program includes −
Good efficiency ensures higher performance.
#Functional programming code
The efficiency of a programming code is directly proportional to the algorithmic efficiency and the execution speed. Supports both "Abstraction over Data" and "Abstraction over Behavior". For example: For-each loop in JavaĮxecution order of statements is not so important.Įxecution order of statements is very important. It uses "Loop" concept to iterate Collection Data. It uses "Recursion" concept to iterate Collection Data. Its methods can produce serious side effects.įlow Control is done using function calls & function calls with recursionįlow control is done using loops and conditional statements. The following table highlights the major differences between functional programming and object-oriented programming − Functional Programming Lisp is used for artificial intelligence applications like Machine learning, language processing, Modeling of speech and vision, etc.Įmbedded Lisp interpreters add programmability to some systems like Emacs.įunctional Programming vs. As it does not have state, you need to create new objects every time to perform actions.įunctional Programming is used in situations where we have to perform lots of different operations on the same set of data. Lazy Evaluation − Functional programming supports Lazy Functional Constructs like Lazy Lists, Lazy Maps, etc.Īs a downside, functional programming requires a large memory space. Supports Nested Functions − Functional programming supports Nested Functions. As a result, such programs are more efficient. Such codes support easy reusability and testability.Įfficiency − Functional programs consist of independent units that can run concurrently. One can program "Functions" to work parallel as "instructions".
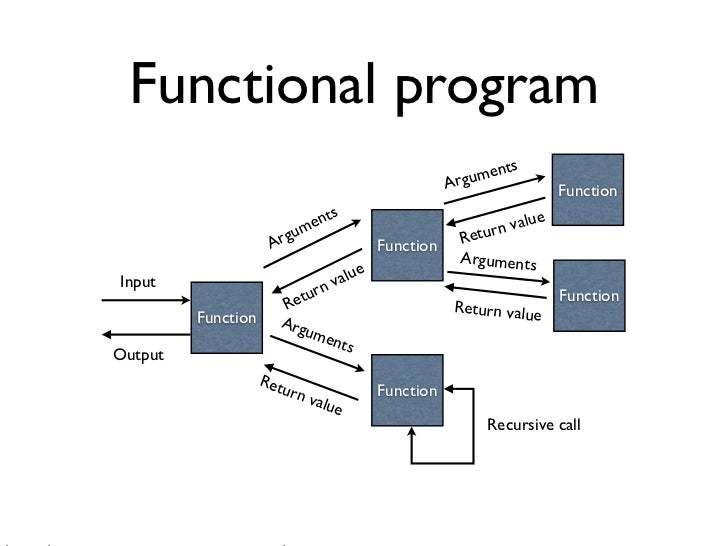
Like OOP, functional programming languages support popular concepts such as Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Polymorphism.įunctional programming offers the following advantages −īugs-Free Code − Functional programming does not support state, so there are no side-effect results and we can write error-free codes.Įfficient Parallel Programming − Functional programming languages have NO Mutable state, so there are no state-change issues. They directly use the functions and functional calls. The most prominent characteristics of functional programming are as follows −įunctional programming languages are designed on the concept of mathematical functions that use conditional expressions and recursion to perform computation.įunctional programming supports higher-order functions and lazy evaluation features.įunctional programming languages don’t support flow Controls like loop statements and conditional statements like If-Else and Switch Statements. Impure Functional Languages − These types of functional languages support the functional paradigms and imperative style programming.
Pure Functional Languages − These types of functional languages support only the functional paradigms. Some of the popular functional programming languages include: Lisp, Python, Erlang, Haskell, Clojure, etc.įunctional programming languages are categorized into two groups, i.e. Functional programming is based on mathematical functions. Functional programming languages are specially designed to handle symbolic computation and list processing applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
